A pure substance
-made up of only one substance.
-not mixed with any other substance.
e.g. white diamond is only made of carbon.
Air is not a pure substance-mixture of gases such as carbon dioxide, oxygen, nitrogen and water vapor.
Purity is important in food and beverages. Chemicals are added to make them last longer, look more attractive or taste better (preservatives and dyes).
Tests for purity:
- check the substances' melting points and boiling points.(solid that has exact and constant melting point is pure- a pure solid will melt completely at one temperature)
-> impurities affects the melting point of a substance by lowering its melting point or cause melting to take place over a wider range of temperatures.
constant boiling point: if liquid is impure, its boiling point will increase and also boil over a range of temperatures.(greater amount of impurities, the higher the boiling point of liquid)
(If the pressure on liquid is increased, the boiling point is also raised/ If pressure is decreased, boiling point is also lowered.)

2. use Chromatography.(also used to test for safe food dyes/coloring)
Chromatography is the technique of using a solvent to separate a mixture into its components.(can be used to separate dyes in ink, pigments in plants, amino acids obtained from proteins, to identify poisons or drugs and to detect banned substances in food)
-> Paper chromatography(small drop of ink placed in the middle of filter paper
-> addition of ethanol causes the spot of ink in the middle to spread out into different colored rings. Each ring represents a different dye that made up the ink.
Another method:
The solvent ascends or travels up the chromatography paper.
-> the solvent continues to travel up the paper and dissolves the dyes.
-a dye not very soluble will not be carried far along the paper while a dye very soluble will be carried far along the paper(depending on solvent)
Colored spots are left in different places on the chromatography paper at the end of the experiment.
Special points:
1) Mixture must be above solvent level-> prevents mixture from dissolving directly into solvent.
2) Mixture dot needs to be small-> too much ink will smudge the chromatogram.
3) Starting line has to be drawn in pencil-> graphite(pencil lead) will not dissolve in solvent and will not spoil/interfere in results of chromatography.
4) Solvent should keep traveling upwards-> ensure good separation of ink components.
Separating a Solid from a Liquid
Decanting: simplest way to separate water from pebbles is to pour the water away.
-> used to separate a dense, insoluble solid from a liquid.
-> Decanting to separate a dense, insoluble solid from a liquid.
Filtration: used to separate small solid particles from a liquid.
e.g. to separate sand and water
e.g. of small solid particles: sand, clay, dust, particles and precipitates

A solid can be separated from a liquid by filtration because the filter paper acts as a sieve. A liquid can pass through the pores of the filter paper but a solid could not.
Solid that remains on filter paper-> residue
liquid or solution that passed through filter paper-> filtrate
Evaporation to Dryness and Crystallization:
Many substances such as salt, dissolves in water to form solutions. To separate such substances, filtration is not used, instead we evaporate water from the solution.
e.g. When salt solution is evaporated to dryness, solid salt is recovered.(used to recover salt from seawater)
However, many substances decompose when they are heated strongly. For example, sugar will decompose when it is heated strongly. Most crystals give off water to become powder when heated. Evaporation to dryness is bot a good method of purification(after water removed, any soluble impurities present will be left on the crystals)
- the best method of obtaining a pure solid sample from the solution is crystallization.
How?- water is removed by heating the solution and heating is stopped when hot saturated solution is formed. The resulting solution is allowed to cool to room temperature and the dissolved solid will be formed as pure crystals.
To test for saturated solution- a clean glass rod is dipped into the solution and removed. A small amount of solution on the rod will cause crystals to form on the rod as it cools.
(saturation point/ crystallization point)
Example of obtaining copper(II) sulphate crystals from copper(II) sulpphate solution:
copper(II) sulphate solution-------(heat until mixture is saturated)-----------> saturated copper(II) sulphate solution---------(allow solution to cool)-----------> copper(II) sulphate crystals+ solution(contains soluble impurities)-------(filter the mixture)-------> copper(II) sulphate crystals
-> Paper chromatography(small drop of ink placed in the middle of filter paper
-> addition of ethanol causes the spot of ink in the middle to spread out into different colored rings. Each ring represents a different dye that made up the ink.
Another method:
The solvent ascends or travels up the chromatography paper.
-> the solvent continues to travel up the paper and dissolves the dyes.
-a dye not very soluble will not be carried far along the paper while a dye very soluble will be carried far along the paper(depending on solvent)
Colored spots are left in different places on the chromatography paper at the end of the experiment.
Special points:
1) Mixture must be above solvent level-> prevents mixture from dissolving directly into solvent.
2) Mixture dot needs to be small-> too much ink will smudge the chromatogram.
3) Starting line has to be drawn in pencil-> graphite(pencil lead) will not dissolve in solvent and will not spoil/interfere in results of chromatography.
4) Solvent should keep traveling upwards-> ensure good separation of ink components.
Separating a Solid from a Liquid
Decanting: simplest way to separate water from pebbles is to pour the water away.
-> used to separate a dense, insoluble solid from a liquid.
-> Decanting to separate a dense, insoluble solid from a liquid.
Filtration: used to separate small solid particles from a liquid.
e.g. to separate sand and water
e.g. of small solid particles: sand, clay, dust, particles and precipitates

A solid can be separated from a liquid by filtration because the filter paper acts as a sieve. A liquid can pass through the pores of the filter paper but a solid could not.
Solid that remains on filter paper-> residue
liquid or solution that passed through filter paper-> filtrate
Evaporation to Dryness and Crystallization:
Many substances such as salt, dissolves in water to form solutions. To separate such substances, filtration is not used, instead we evaporate water from the solution.
e.g. When salt solution is evaporated to dryness, solid salt is recovered.(used to recover salt from seawater)
However, many substances decompose when they are heated strongly. For example, sugar will decompose when it is heated strongly. Most crystals give off water to become powder when heated. Evaporation to dryness is bot a good method of purification(after water removed, any soluble impurities present will be left on the crystals)
- the best method of obtaining a pure solid sample from the solution is crystallization.
How?- water is removed by heating the solution and heating is stopped when hot saturated solution is formed. The resulting solution is allowed to cool to room temperature and the dissolved solid will be formed as pure crystals.
To test for saturated solution- a clean glass rod is dipped into the solution and removed. A small amount of solution on the rod will cause crystals to form on the rod as it cools.
(saturation point/ crystallization point)
Example of obtaining copper(II) sulphate crystals from copper(II) sulpphate solution:
copper(II) sulphate solution-------(heat until mixture is saturated)-----------> saturated copper(II) sulphate solution---------(allow solution to cool)-----------> copper(II) sulphate crystals+ solution(contains soluble impurities)-------(filter the mixture)-------> copper(II) sulphate crystals
Separating Solids
Filtration: A mixture of for example, sand and salt(both solids), can be separated by filtration using water as the solvent.- Salt is soluble in water but sand is not.
Procedure
1. Pour distilled water into mixture of salt and sand. Stir and warm the mixture.
2. Pour warm mixture into a filter funnel lined with filter paper. Collect filtrate.
3. Wash residue with a little distilled water to remove all of the salt solution from it. The residue is sand.
4. Pour filtrate into evaporating dish and evaporate filtrate to dryness. Salt is left in the evaporating dish.
Magnets can be used to separate solids.
- steel is also magnetic
- In recycling, magnets are used to recover magnetic materials from domestic waste
Separating a Liquid from a Solution
When a solid dissolves in a solvent, a solution is formed. E.g. salt solution, sugar solution.
To collect solute from the solution- evaporate the solvent.
Obtaining the solvent....
- A pure solvent can be separated from a solution by simple distillation.(boiling a liquid and condensing the vapor)
Diagram of simple distillation:
1. The solution boils in the distillation flask, water vapor rises to enter the condenser.
2. In the condenser, water vapor is cooled and condenses to change back into pure water.
3. Pure water is collected as distillate in a beaker.
4. The salt solution remaining in the distillation flask becomes more concentrated as the distillation proceeds. If the distillation proceeds, a solid residue of salt will be left in the flask.
As the salt solution is heated, its temperature increases. When the solution finally boils, the thermometer records a temperature 100 degrees Celsius( temperature of the water vapor) The temperature remains unchanged until all the water has boiled off.
Separating Liquids
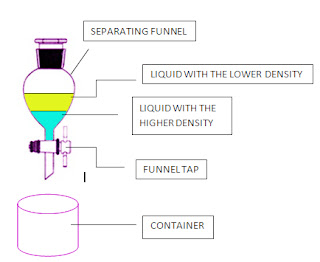
Liquids that do not dissolve in each other are described as immiscible. Oil and water are immiscible in each other.
To separate immiscible liquids, we use a separating funnel.
E.g. oil and water
Separating miscible liquids...
e.g. ethanol and water- mixed together to form a solution.
-separated by a technique called fractional distillation
(a column called the fractionating column is attached to the flask and condenser. Many glass beads in the fractionating column provide a large surface area for vapor to condense on. A fractionating column may be filled with plates or a spiral, instead of glass beads)
During fractional distillation, the liquid with the lowest boiling point will distill over to the condenser first. Vapors of liquids with higher boiling points condense along the inner wall of the fractionating column and re-enter the flask.
-> diagram of fractional distillation
-> water vapor condenses in fractionating column and drops back into the flask. Ethanol which has a lower boiling point than water, reaches the upper part of the column and is distilled over. (At this stage the thermometer would show a constant temperature of 78 degrees celsius- boiling point of ethanol)
-> ethanol is collected as the distillate in the receiver.
- fractional distillation is used in industries to obtain nitrogen, argon and oxygen from air.
- it can also be used to separate mixtures of liquids such as crude oil.
- ethanol is formed when glucose solution undergoes fermentation in the presence of yeast. Ethanol and glucose solution can be separated by fractional distillation.
Summary
Crystallization(main features):
1) Makes the substance pure.
2) Solution should be saturated.
3) Change in state of substance from aqueous(a.q.)-> substance that has dissolved in water to solid.
Chromatography(main features):
1) To separate a mixture.
2) To find out the number of components.
3) Depends on solubility of compounds or substances in a solvent.
E.g. TRAVELS...
FAST (Higher solubility)
SLOW
Filtration:
1) Differentiate between differently-sized substances.











No comments:
Post a Comment